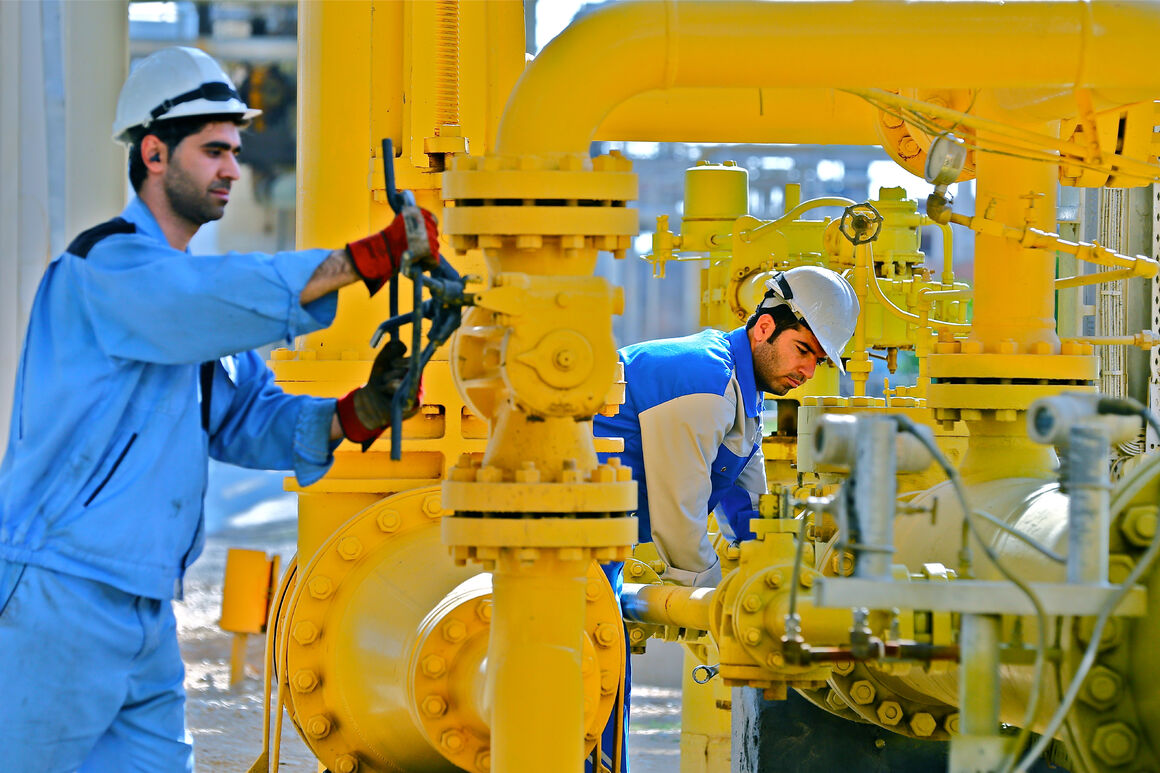
Iran boasts one of the world’s largest natural gas reserves, second only to Russia, holding over 33 trillion cubic meters of proven reserves. Natural gas represents a critical element of Iran’s economy, energy security, and geopolitical strategy.
Iran’s vast reserves are primarily concentrated in the South Pars/North Dome field, shared with Qatar. South Pars alone accounts for nearly 40% of Iran’s total gas reserves. Over the past two decades, development in this region has significantly increased, driven by government efforts to capitalize on these vast resources and achieve energy self-sufficiency.
The Iranian gas industry functions predominantly through the National Iranian Gas Company (NIGC), responsible for managing the country’s gas processing plants, pipeline networks, distribution systems, and domestic and export sales. This comprehensive network ensures that natural gas plays a pivotal role in the domestic energy mix, accounting for nearly 70% of total energy consumption.
Iran uses its vast gas reserves primarily for domestic electricity generation, industrial consumption, residential heating, and petrochemical production. Natural gas also underpins Iran’s broader energy security strategy, aiming to reduce dependence on oil products, thus freeing up more crude oil for export.
Despite having extensive resources, Iran faces significant challenges, including international sanctions, limited investment in infrastructure, and technological limitations, hindering full exploitation and export capacity. Nevertheless, Iran continues to expand its production capabilities, pipeline networks, and export routes, targeting markets in neighboring countries and beyond.
Strategically, Iran seeks to position itself as a key regional player in natural gas exports, leveraging pipelines and potential LNG developments to increase its influence in global energy markets. With geopolitical tensions often influencing market dynamics, Iran’s ability to navigate these complexities remains critical.
In conclusion, Iran’s natural gas industry stands as a cornerstone of the country’s energy economy. Continued investment and international cooperation could significantly enhance its global competitiveness and economic potential.