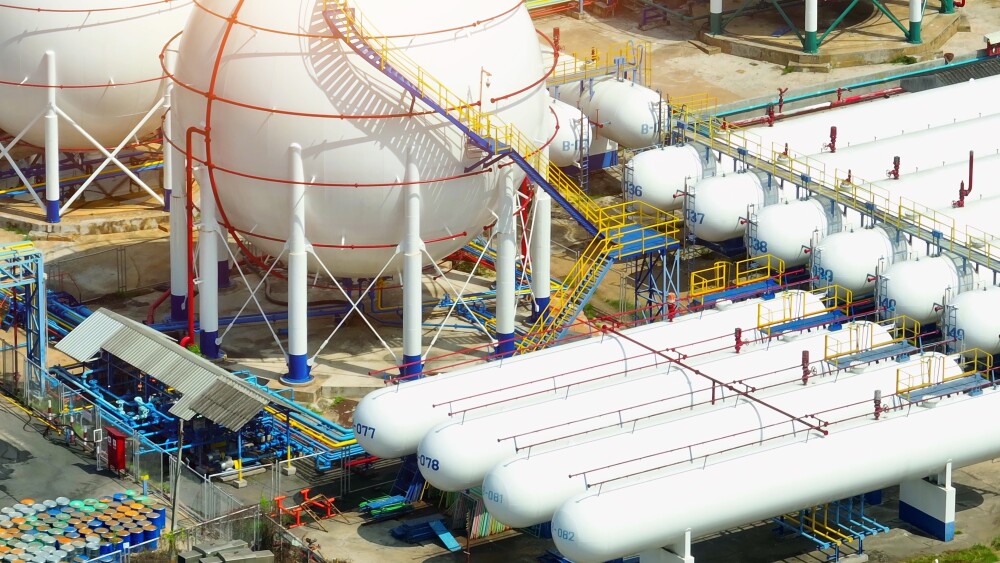
Natural gas plays a crucial role in Iran’s economy, significantly impacting employment, government revenue, and overall economic development. With the second-largest natural gas reserves globally, Iran leverages this resource to enhance economic stability and growth.
Revenue from natural gas significantly contributes to Iran’s GDP, funding various national development projects, infrastructure improvements, and social programs. The industry creates extensive employment opportunities, directly employing thousands in extraction, processing, transportation, and distribution sectors.
Natural gas supports other critical economic sectors, notably petrochemicals, steel, cement, and electricity generation, enhancing their competitiveness by providing low-cost, reliable energy. Consequently, industrial sectors relying heavily on natural gas have flourished, contributing to broader economic diversification efforts away from traditional oil dependency.
Export revenues from natural gas, though still limited due to international sanctions, provide valuable foreign currency earnings crucial for maintaining economic stability amid global market fluctuations. Iran primarily exports gas to regional markets, notably Iraq and Turkey, and actively seeks to expand exports to neighboring countries through pipeline development.
However, sanctions and geopolitical challenges substantially limit Iran’s capacity to fully capitalize on its gas resources economically. Restricted access to foreign investment and technology hampers productivity and export potential, significantly impacting economic growth opportunities.
Future economic prospects remain closely tied to international diplomacy and sanctions relief, potentially allowing substantial foreign investments. Successful international agreements could dramatically increase export capacities, contributing significantly to Iran’s economic development and international trade profile.
In conclusion, natural gas significantly bolsters Iran’s economy, driving employment, industrial growth, and international trade. Future economic benefits hinge largely on the evolving geopolitical landscape and investment conditions.